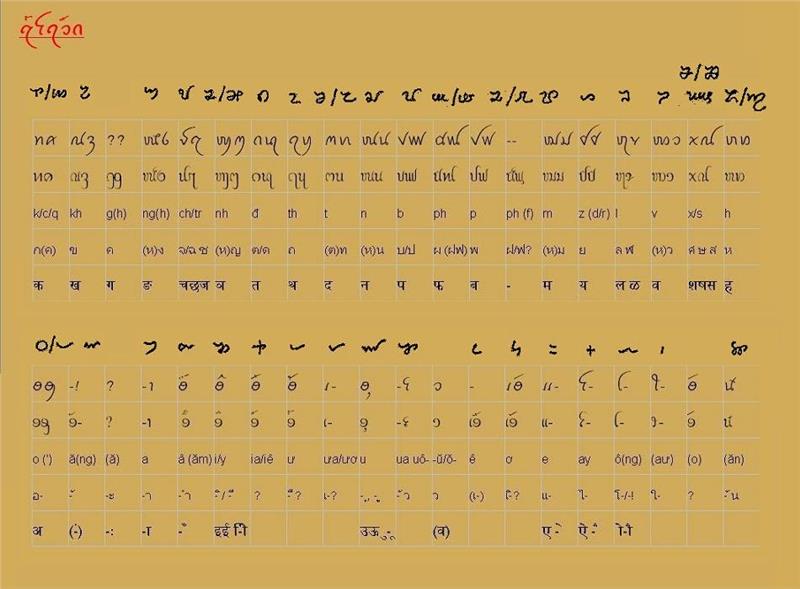
 |
Ancient Vietnamese script
Source: alotrip.com
|
Linguistic Classification
Vietnamese
was identified more than 150 years ago as part of the Mon-Khmer
branch of the Austroasiatic language family (a family that also
includes Khmer, spoken in Cambodia, as well as various tribal and regional
languages, such as the Munda and Khasi languages spoken in
eastern India, and others in southern China).
Later, Muong was found to
be more closely related to Vietnamese than other Mon–Khmer languages, and a
Viet–Muong subgrouping was established, also including Thavung ,
Chut, Cuoi, etc. The term "Vietic" was
proposed by Hayes (1992), who proposed to redefine Viet–Muong as referring
to a subbranch of Vietic containing only Vietnamese and Muong. The term "
Vietic" is used, among others, by Gerard Diffloth, with a slightly
different proposal on subclassification, within which the term "Viet–Muong"
refers to a lower subgrouping (within an eastern Vietic branch) consisting of
Vietnamese dialects, Muong dialects, and Nguon (of Quang Binh Province).
As a National Language
 |
Percentage
of Vietnamese people, by province
<20%
20%–40%
40%–60%
60%–80%
80%–95%
>95%
Source: wikipedia.org |
Vietnamese (tiếng
Việt) is an Astroasiastic language that
originated in Vietnam, where it is the national and official language. It is
the native language of the Vietnamese (Kinh) people, as well as a first or
second language for the many ethnic minorities of Vietnam
. As a result of Vietnamese emigration and cultural influence, Vietnamese
speakers are found throughout the world, notably in East and Southeast Asia,
North America, Australia and Western Europe.
In addition to this, it is the
Austroasiatic language with by far the most speakers, several times as many as
the rest of the family combined. Its vocabulary has borrowings from Chinese,
and it formerly used a modified set of Chinese characters called Chữ Nom given
vernacular pronunciation. The Vietnamese alphabet (chữ quốc ngữ) in use today
is a Latin alphabet with additional diacritics for tones and certain letters.
In the Czech Republic,
Vietnamese has been recognized as one of 14 minority languages, on the basis of
communities that have resided in the country either traditionally or on a
long-term basis. This status grants Czech citizens from the Vietnamese
community the right to use Vietnamese with public authorities and at courts
anywhere in the country. Moreover, it also grants the use of Vietnamese in
public signage, election information, cultural institutions, and access to
legal information and assistance in municipalities where at least 10% of the
population is of the minority group.
As
a Foreign Language
 |
Global Distribution of Vietnamese speakers
Source: https://www.alotrip.com
|
Vietnamese
is increasingly being taught in schools and institutions outside of Vietnam. In
countries with strongly established Vietnamese-speaking communities such as
Australia, Canada, France, and the United States, Vietnamese language education
largely serves as a cultural role to link descendants of Vietnamese immigrants
to their ancestral culture. Meanwhile, in countries near Vietnam such as
Cambodia, Laos, South Korea, and Thailand, the increased role of Vietnamese in
foreign language education is largely due to the growth and influence of
Vietnam's economy.
Since the 1980s, Vietnamese
language schools (trường Việt ngữ) have been established for youth in many
Vietnamese-speaking communities around the world, notably in the United
States.
Historic and stronger trade
and diplomatic relations with Vietnam and a growing interest among the French
Vietnamese population (one of France's most established non-European ethnic
groups) of their ancestral culture have also led to an increasing number of
institutions in France, including universities, to offer formal courses in the
language.
Since the late 1980s, the Vietnamese
German community has enlisted the support of city governments to bring
Vietnamese into high school curricula for the purpose of teaching and reminding
Vietnamese German students of their mother-tongue. Furthermore, there has also
been a number of Germans studying Vietnamese due to increased economic
investment in Vietnam.
Vietnamese is taught in
schools in the form of dual immersion to a varying degree in Cambodia,
Laos, and the United States. Classes teach students subjects in
Vietnamese and another language. Furthermore, in Thailand, Vietnamese is one of
the most popular foreign languages in schools and colleges.
Source: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Vietnamese_language
Disclaimer: The author does not claim the OWNERSHIP of any of the information above.


No comments:
Post a Comment